In this article you can find out why varicose veins in the pool is considered a separate disease and not a form of varicose veins on your legs, the disease may also occur, and why. Symptoms, diagnosis, pathology, as it is properly treated, the chances of recovery.

Varicose veins of the pelvis – the weakening of the walls of internal or external veins in the pelvic area, which is the excessive extension of the diameter. Varicose changed veins are not able to provide the outflow of the blood in the pelvic organs, which leads to the stagnation or the total destruction of the vessel wall. As a result, damage to the structure and functions of the female reproductive system.
Early stages of the disease, because only minor discomfort in the vulva, and abdomen. The women advanced form of pelvic varicose veins suffer from constant, severe pain, various gynecological diseases, infertile, cosmetic defect in the form of tortuous dilated venous nodules on the perineum, labia, or entrance to the vagina.
The disease can be cured, but to prevent relapse prevention is necessary for life. In dealing with this problem together vascular surgeons, obstetrician-gynecologist.
Varicose veins of small pelvis in men than women doesn't happen. But such a disease exists – venous. Mechanisms, and the symptoms are similar to the pelvic varicose veins. Dilatation occurs in the left testicle to the spermatic cord due to the fact that the left Vienna eggs in stagnant blood. He threw back the left renal vein, which flows into Vienna.
The essence of the disease, how serious it is
The external and internal female genital organs - krovosnabjaemah. In order to have sufficient blood flow, you need a strong network of venous vessels. Therefore, the venous system of the pool of women well-developed. Every vein of a solid wall, provided with valves connected with passing near the veins. The whole form a coherent venous network in the pelvic region which collects blood, the perineum, the external genitals (vulva, vagina), special structures (ovaries, uterus), transportorul the bottom Polow vein.
Varicose changed veins of the pelvis differ from the healthy in that:
- Extended diameter;
- They are full of blood;
- It is extremely convoluted;
- You have to be protruding in the form of nodes;
- Powerless, weak.
Pelvic veins affected by varicose veins, collect the blood in the external genital organs and other organs, but I don't know, to transport, to larger vessels (the Vena cava). This leads to the fact that the blood stuck to the pool, penetrating through the venous wall affect the tissues, which needs to flow. They become swollen, inflamed and lose function.
But most of all, varicose veins are the pool dangers:
- Various diseases of the ovaries;
- Uterine bleeding disorders, or other;
- Infertility, complications, inability to natural childbirth;
- Formation of blood clots in the lumen of the varicose changed veins, and a threat to the separation of the place of education, as well as the migration of the heart, the pulmonary vessels. This is the most dangerous complication, life-threatening – pulmonary embolism (PE).
Reason
Basically varicose veins of the pelvis happens Mature women:
- Up to 20 years – 20%;
- 20-30 years – 30%
- 30 – 45 years – 50%
Mechanisms of varicose degeneration of the venous system to the pool:
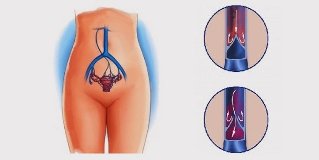
- (80%). These are the main veins that collect the blood, the uterus, ovaries, take him directly to a hollow (right) or the kidney (left), Vienna. If an error occurs, completely blocking the venous outflow.
- A uniform weakening or destruction of the venous wall, the pelvic veins – these are all at the same time who is not able to contract, driving the blood into the cover classes.
- Reverse reflux of blood in the deep vein of the thigh, the superficial sexual vein, which collects blood from the perineum and the external genital organs, prevents the outflow. As a result, the pressure increases, the trunk and all tributaries of the varicose expanded.
The direct reason that the launch of these mechanisms could be the following:
- Congenital weakness or dysplasia (underdevelopment) of the venous wall and valves.
- Hormonal changes in the woman's body (puberty, pregnancy, menopause, ovarian disease).
- Frequent inflammation, endometriosis, surgery, adhesions in the pelvis.
- Moved to thrombosis, thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins.
- It's hard physical work.
- Prolonged lying down or sitting.
- Overweight.
- Pregnancy, childbirth.
- Regular interruption of intercourse for many years, especially in the absence of the orgasm.
- Bend uterus posteriorly, or sooner.
- Pelvic tumors.
- Prolapse of the uterus.
If the varicose veins classification
The anatomical reasons (prevalence) of varicose veins of the pelvis be classified into three groups:
- The venous congestion in the pelvis;
- Dam varicose veins, etc.;
- In combined form.
To reflect pathological changes of the disease is divided into three levels:
- First, the dilated blood vessels of any organ plexus of the pool may not exceed a diameter of 0.5 cm, an extremely convoluted.
- The second is the diameter of the blood vessels increased to 1 cm, the process covers not only the plexus organs(uterus, ovaries), but some of them (okolomatocnah cellulose).
- The third expansion (ectasia) of more than 1 cm, affecting all vessels – blood, close to the body, torso (the trunk of the ovarian vein).
The higher degree of the disease, the worse dilated veins and heavier congestion in the pool.
Typical symptoms
The women of varicose veins, the pool note:
- Persistent or recurring pain in the abdomen, worse in the evening or after exertion, especially in the second half of the cycle (close to monthly). 3 degrees of pain is very strong.
- Itching, burning sensation, swelling, discoloration of the genital organs.
- Painful periods or intercourse.
- Heavy menstruation, uterine bleeding, irregular cycle.
- The inability to get pregnant.
- Thick twisted veins in the region of the perineum, labia.
- Frequent painful urination.
- Pronounced symptoms of premenstrual syndrome.

Diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis is carried out:
- Ultrasound through the abdomen, and the vagina (transvagin ally) advanced sensors – Doppler, duplex treatment of veins of the pelvis. The simplest, most informative way.
- Endovascular venography the introduction of the special drugs of the ovarian vein.
- Computed tomography the contrast.
- A diagnostic laparoscopy.
Treatments
Varicose veins of the pelvis together to treat the vascular surgery or ob-gyn. The modern concepts, the treatment consists of the following areas:
- Normalization lifestyle;
- Conservative medical treatment;
- Compression, or other therapy;
- Surgical treatment.
Cure of varicose veins of the pelvis. The specialists make an individual treatment plan, the patient woman to stick to the life, recommendations for treatment, prevention.
1. Normalization of lifestyle
Because of the bad life is a prerequisite, as well as the direct causes of varicose pelvic veins, the normalization helps to restore:
- Excludes long stay standing or sitting (more than 2-3 hours without a break).
- Do not lift heavy objects and refrain from strenuous physical activity.
- One day, under the management practices of the pool (practice birch, bicycle), or just lay down for 10-15 minutes with elevated above the level of the body by the pool.
- To reduce the weight (obesity).
- Don't take a hot bath, replace it with a cold shower.
- Refrain from alcohol and Smoking.
2. Drug therapy
Treatment of varicose veins pelvic any extent not possible without medical help. The first floor of a major medical event, while the second and the third complements the comprehensive treatment.
Used such drugs:
- Special medicines that strengthen the blood vessels.
- Anticoagulants – thin blood to facilitate the progress of the ship.
- Drugs that improve the microcirculation.
Additional groups of medicines prescribed, having regard to the existing differences in the body:
- Preparations of female sex hormones (hormonal disorders).
- Analgesic, anti-inflammatory.
- Drugs to stop blood styptic agents in the treatment of uterine bleeding.
3. Compression therapy
One of the effective tool for the treatment of varicose veins of the vulva, the dam is a compression effect. This method principle is similar to the use of elastic bandage for varicose veins of the legs. Compression (compression) of the superficial veins on the outside contributes to the evacuation of the blood. To create this effect you can special tights or pants, compression therapy stockings. You can buy special pharmacies, shops, salons, medical products individually to choose the correct size, the force of the compression.
Varicose veins – a puncture of the varicose veins with the introduction of a special licence must be the drugs, because of the glue. This treatment is carried out, the external (subcutaneous) pelvic varicose veins without a hospital treatment in the hospital. The internal veins can also be treated, but this procedure is technically more complicated, takes place in the operating room.
4. Surgical treatment
Varicose veins of small pelvis may be better treated with surgery if:
- 2-3 degrees of the disease;
- The rapid progression of the disease;
- Planning pregnancy;
- Expressed pain syndrome;
- Regular uterine bleeding and other gynecological diseases.
Main operations on the pelvic varicose veins:
- Laparoscopic – a special operation through the punctures of the abdomen. Perform the ligation, the intersection, or the removal of the ovarian vein. This eliminates the backward reflux of blood through.
- Removal of varicose veins through small puncture or cut the skin removal, as amended by vein saphenous is tied to the external pudendal vein to the point where the femoral vessels.
- Gynecological intervention – removal of tumors, removal of bend of the uterus.
Forecast
If we don't treat the varicose veins of the pelvis, over time, they expand even more (95%), which faces dangerous complications. The remaining 5% of women under the skin varicose veins of the perineum, 1-2 degrees, from which it turns out, after the birth, the pathology is not reinforced, but it never goes away.
If you treat the disease, that can achieve full recovery (10-50% depending on the degree) or significant improvement (45-50%), especially in the case of the combined surgical techniques conservative. But in any case, after a comprehensive treatment of lifelong prophylaxis, that compliance with recommendations on lifestyle, medication, or intermittent compression to support weakened veins.





































